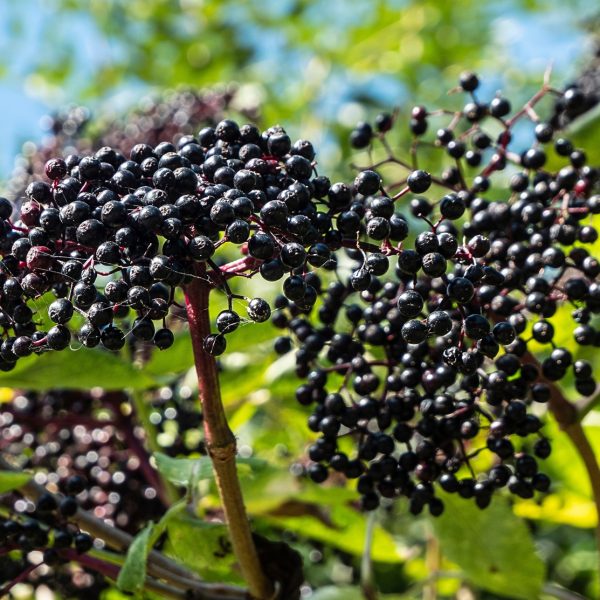
-
Herb overview
Safety
Avoid during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Sustainability
Low risk/Green
FairWild certified sources availableKey constituents
Flavonoids
Phenolic acidsQuality
Native to Europe
Wild-harvested
Contamination risks from pollutants in the local environmentKey actions
Diaphoretic
Anti-inflammatory
Febrifuge
AntiallergicKey indications
Colds and flu
Hayfever
Fever
SinusitisKey energetics
Hit
DryPreperation and dosage
Flower
Tincture (1:5 | 40%): take 6–12 ml daily
Infusion/decoction: One tablespoon of dried elderflowers per cup
-
How does it feel?
Elderflowers have a beautiful and unique aromatic quality. Its creamy white fragrant blossoms are sweet, cooling and mildly bitter to taste. The aromatic oils in elderflower are well preserved as a dried herb and also preserve well in cordial and tincture. The fresh tea has a fresh aromatic flavor with an additional mild pungency.
-
Into the heart of elderflower
 Not only can Elderflower be used in acute and first aid situations as discussed above, but elderflower also has a gently relaxant effect which may be applied for those experiencing nightmares and disturbed sleep, useful for both adults and children.
Not only can Elderflower be used in acute and first aid situations as discussed above, but elderflower also has a gently relaxant effect which may be applied for those experiencing nightmares and disturbed sleep, useful for both adults and children.Described by Brooke (2018), as a herb that increases sweating, elderflower can also aid the skin, helping to clear the pores by removing impurities. For this, a hot infusion is most often given for the diaphoretic (sweat inducing) action. Congruently, Grieve (1984) refers to the use of elderflower as an infusion used on the skin, explaining that it can improve the complexion and brighten the skin.
Energetically, in terms of Western Herbal Medicine, Elderflower is hot and dry, however, when drank as a hot tea for increasing the output of fluid by sweating, elderflower exhibits a cooling effect. An example of how different preparations of a herb can display varied actions. Either as a result of how the compounds interact with the extraction method, the deliverance of the compounds by the predation type mixed with the energetic characteristics of the preparation itself.
In Ayurvedic view, elderflowers are referred to as being bitter, pungent and cooling, reducing kapha and pita and having a neutral or mixed effect in vata. It seems again that alternative narratives to this plant’s energetic actions are held by the different energetic systems in Herbal Medicine. Most unanimous is that this plant has an overall cooling effect, rather than directly heating.
-
What practitioners say
 Respiratory system
Respiratory systemElderflower is particularly useful for influenza or the common cold. Indicated for all manner of catarrhal inflammations in the upper respiratory tract, this would include viral and allergic conditions, such as sinusitis, tonsillitis and hay fever. Elderflowers can also be used where there is congestion in the inner ear.
Immune system
Elderflower is great for the management of fevers. As opposed to the orthodox approach of treating fevers which is to reduce temperature/ symptoms, the herbal / holistic approach is rather to support and moderate this important immunological process, with a view to improving overall recovery outcomes. Fevers are the bodies natural response to pathogens (viral/ bacterial). In basic terms, the rise in blood temperature during a fever, is the body’s attempt to create an inhospitable environment for pathogens to survive.
Sweating also increases during a fever to further improve elimination from the blood whilst also diffusing and heat. At the point where we start to sweat during a fever, our body is doing incredible work to fight off the bacteria or virus. Elderflower directly supports these processes through its anti-inflammatory and diaphoretic actions.
Peppermint and yarrow are often combined with elderflower to support through influenza and the common cold, particularly through the fever stage.
Please note: Fevers can be a sign of serious health conditions that need immediate medical attention, if the cause of fever is not identified as being of the acute viral nature (common cold/ influenza). One must be sure to seek professional advice where symptoms do not improve in any circumstance.
Eliminatory system
Through its diaphoretic action elderflower can support detoxification through the skin, therefore as an adjunctive to work alongside herbs that improve hormonal balance and increase the lymphatic detoxification. Elderflower may therefore be useful as part of an approach for skin conditions and overall movement of body fluids.
Circulatory system
Elderflower may also be useful for oedema and other congestive conditions of the circulatory system, by its ability to increase the output of fluid. Elderflower is described as a peripheral vasodilator, meaning that it increases dilation in the peripheral capillaries, which may be useful where there is poor circulation to the extremities (hands and feet).
-
Elderflower research
 Much of the research available into the immunological effects of Elder, focuses on the elderberry. However an in vitro study on both extracts of Elderberry and Elderflower constituents exhibited promising inflammatory modulating activity. It must be noted though that unfortunately clinical trials are lacking for elderflower.
Much of the research available into the immunological effects of Elder, focuses on the elderberry. However an in vitro study on both extracts of Elderberry and Elderflower constituents exhibited promising inflammatory modulating activity. It must be noted though that unfortunately clinical trials are lacking for elderflower.A specific group of compounds called phenolic compounds, isolated in elderflower are found to be highly antioxidant in a review carried out in 2015, the action of these antioxidants is to protect against cellular damage from free radicals, whilst improving cellular health and function.
An in vitro study investigating the action of peptic polysaccharides in extracts of elderflower, found positive outcomes for enhancing cellular immunity, supporting to the well documented belief that elderflower is a valuable medicine for the treatment of acute viral infections.
Another in vitro stem cell study was carried out into the effects of elderflowers potential neuroprotective benefits, the study provided insights into the mechanisms by which elderflower extract could suppress neurotoxicity elicited by environmental and genetic stressors.
-
Traditional actions
Herbal actions describe therapeutic changes that occur in the body in response to taking a herb. These actions are used to express how a herb physiologically influences cells, tissues, organs or systems. Clinical observations are traditionally what have defined these actions: an increase in urine output, diuretic; improved wound healing, vulnerary; or a reduction in fever, antipyretic. These descriptors too have become a means to group herbs by their effects on the body — herbs with a nervine action have become the nervines, herbs with a bitter action are the bitters. Recognising herbs as members of these groups provides a preliminary familiarity with their mechanisms from which to then develop an understanding of their affinities and nuance and discern their clinical significance.
-
Traditional energetic actions
Herbal energetics are the descriptions Herbalists have given to plants, mushrooms, lichens, foods, and some minerals based on the direct experience of how they taste, feel, and work in the body. All traditional health systems use these principles to explain how the environment we live in and absorb, impacts our health. Find out more about traditional energetic actions in our article “An introduction to herbal energetics“.
Western energetics
-
What can I use elderflower for?
Elderflower is a herb that one should always have in a home herbal first aid kit. This delicate flower is both powerfully anti-catarrhal and anti-inflammatory, making it the perfect for treatment of the common cold or influenza.
By the same means, elderflower is excellent for allergic conditions that cause excess catarrh in the upper respiratory tract, it can be helpful for symptoms of hay fever such as itchy eyes and sneezing.
Safe for all the family, elderflower has a definite affinity for children who are prone to perpetual coughs, colds, runny noses and tonsillitis, although dietary factors should also be considered as possible causes of such condition.
-
Did you know?
The Elder was one of the sacred trees of the Celts, so named Ruis the Elder, the tree of the thirteenth lunar month. There are many folkloric tales of the Elder, which grows natively all over Europe.
-
Botanical description
Elder is a deciduous shrub with pinnate, compound leaves and 3–9 leaflets of ovate or ovate–lanceloate shape and up between 2.5–9 cm long. Each leaflet is toothed and slightly hairy.
The bark is cork-like when mature, and young stems are green and brittle with a spongy white tissue lining the inside.
Flowers are creamy-white and grow in umbels, with five petals on each individual flower (2,17).
-
Common names
- Common Elder
- Black Elder
- Pipe Tree
- Bore Tree
- Hylder, Hylantree (Anglo-Saxon)
- Eldrum (Saxon)
- Ellhorn
- Hollunder (Ger)
- Sureau (Fr) (4)
-
Habitat
Elder is native to Europe and the Azores. It is often found growing in a wide range of habitats in temperate regions, including on forest edges, open woodlands, near bodies of water or on recently disturbed ground (gardens and wastelands) (2,18).
-
How to grow elderflower
Elders are easy to grow. They prefer a location with full sun although they can grow successfully in dappled light – they just need long hours of direct sun exposure. You may find a suitable sapling at a local garden centre to plant out. Elders can tolerate different conditions like poor soil or water logging, however they are intolerant of drought.
Elder planting is done best in well-draining, loamy soil types. Sandy soils should be improved by adding a few inches of organic matter.
Plant your elder early in the spring and be sure to water them regularly so they get off to a good start. Incorporate manure or compost before planting your elder sapling into the ground.
Elders should be left to grow wildly in the first two years of growth. Do not prune and do not bother picking the berries until well established. Thereafter, in early spring you may prune them back and remove all the dead areas. This way, the bushes will grow and produce an abundance of fruit (25).
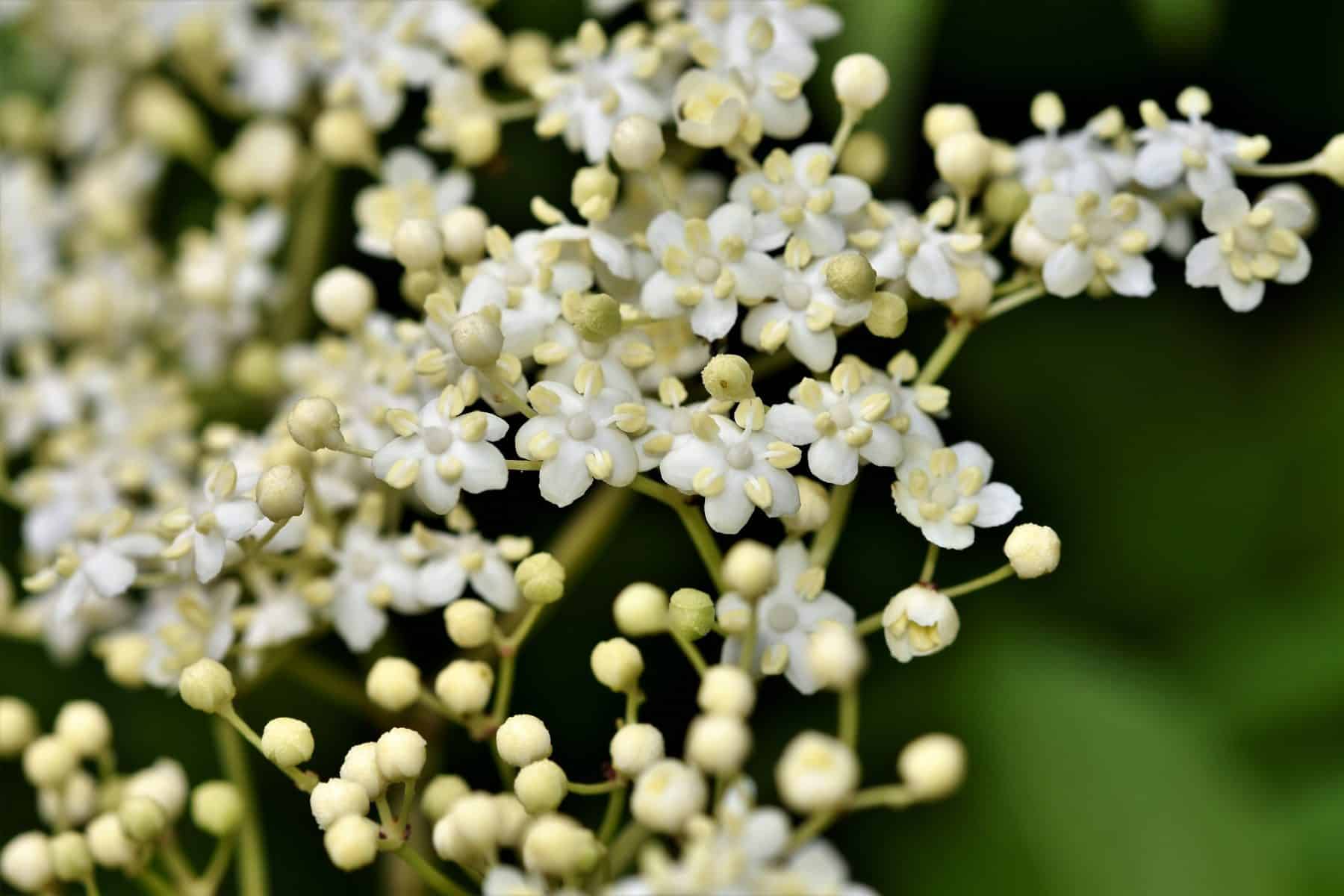


-
Herbal preparation of elderflower
- Tincture
- Infusion
-
Plant parts used
Flowers
-
Dosage
- Tincture (1:5 | 40%): Take 2–4 ml three times a day
- Infusion/decoction: Infuse one tablespoon of dried elderflowers in one cup of boiling water for at least 10 minutes. Strain and drink up to three times a day (2).
-
Constituents
- Flavonoids: Primarily flavonols, rutin, isoquercitrin, astragalin, free quercetin
- Mucilaginous polysaccharides
- Tannins
- Phenolic acids (3%): Chlorogenic, p-coumaric and caffeic acids
- Volatile oil: 76 terpenoid compounds identified
- Triterpenes: Ursolic and oleanolic acids
- Potassium
- Cyanogenic glycosides (1,2,6)
-
Elderflower recipe
Elderflower cordial
A traditional recipe made by many for its sweet floral flavour. Forage flowers when in bloom, usually from May to June, to capture the qualities of elderflower in this delicious cordial to be used throughout the summer and year beyond.
Ingredients
- 25 elderflower heads
- 1 kg sugar
- 2 L water
- 2 unwaxed lemons
How to make elderflower cordial
- Inspect the flowerheads and remove any insects
- Place sliced lemons, sugar and water into a pan and heat slowly, making sure sugar is completely dissolved
- Once dissolved pour liquid over the flowers and leave to infuse overnight
- Strain the mixture and pour into sterilised bottles
- Store in the fridge or cool cupboard
- Enjoy one part cordial to three parts water with ice and a slice of lemon

-
Safety
Avoid during pregnancy and breastfeeding (2,6,16)
-
Interactions
Elderflower may lower blood sugar levels, therefore precaution must be taken in diabetic patients and those taking anti-diabetic medication. It may theoretically also interfere with blood sugar regulation during and post surgery (16).
-
Contraindications
None known (2,6,16)
-
Sustainability status of elderflower

According to the IUCN Red List and Nature Serve elder is classified globally as ‘least concern’ and secure due to its widespread distribution, stable populations and no major threats (19,20).
Habitat loss and over-harvesting from the wild are two of the biggest threats faced by medicinal plant species. There are an increasing number of well-known herbal medicines at risk of extinction. We must, therefore, ensure that we source our medicines with sustainability in mind.
The herb supplement industry is growing at a rapid rate and until recent years a vast majority of medicinal plant produce in global trade was of unknown origin. There are some very real and urgent issues surrounding sustainability in the herb industry. These include environmental factors that affect the medicinal viability of herbs, the safety of the habitats that they are taken from, as well as the welfare of workers in the trade.
The botanical supply chain efforts for improved visibility (transparency and traceability) into verifiably sustainable production sites around the world is now certificated through the emergence of credible international voluntary sustainability standards (VSS).
Read our article on Herbal quality & safety: What to know before you buy and Sustainable sourcing of herbs to learn more about what to look for and questions to ask suppliers about sustainability.


-
Quality control
- Country of origin: Eastern Europe
- How sourced: Wild-harvested
- Risks: Contamination from pollutants in the local environment
- Key marker compounds: Flavonoids, phenolic acids.
Some of the key constituents found in elderflower (Sambucus nigra) include flavonoids (isoquercertin, hyperoside, rutin), phenolic acids (chlorogenic acid), triterpenes (ursolic and oleanolic acids) and a small quantity of essential oil (21,22). The British Pharmacopoeia (BP) requires not less than 0.8% flavonoids expressed as isoquercitroside (23).
The phytochemical constituents in elderflower will vary depending on a range of factors that include geographical origin, genetics, environmental conditions and harvesting season. Elderflowers are often wild collected and a recent study examined the difference in phytochemical constituents between several different cultivated varieties grown in controlled conditions and a wild harvested form collected from a local park (24). In this study, the cultivated varieties varied a lot in phytochemical constituents, although the wild collected form performed best overall, as it was the richest in phytochemical constituents (24). Clearly genetics played a part alongside the environmental conditions that the plant was grown in. If cultivating elderflower, it is important to look into what variety is best to grow for the phytochemical constituents that you are interested in.
The stage of flowering also has an important influence on the content of active constituents in the flowers therefore harvesting at the right time is very important. (24). Elderflower inflorescences should be collected in full bloom (when about 80% of the flowers are open), this is typically in June for the UK (24). By collecting your elderflower at this specific time, it will help ensure that you have selected good quality herbal material. If you are purchasing elderflower, a simple macroscopic assessment (looking at the plant material) will enable you to assess the herb to check that it has the right proportion of open flowers.
-
References
- Mcintyre A. Complete Herbal Tutor : The Definitive Guide to the Principles and Practices of Herbal Medicine (Second Edition). Aeon Books Limited; 2019.
- Fisher C. Materia Medica of Western Herbs. Aeon Books; 2018.
- Brooke E. Woman’s Book of Herbs.; 2018.
- Grieve M. A Modern Herbal.; 1984.
- Thomsen M. Phytotherapy Desk Reference. 6th ed. Aeon Books; 2022.
- Hoffmann D. Medical Herbalism – the Science and Practice of Herbal Medicine. Healing Arts Press; 2003.
- Hedley C, Shaw N. Plant Medicine. Aeon Books; 2023.
- Ho GTT, Wangensteen H, Barsett H. Elderberry and Elderflower Extracts, Phenolic Compounds, and Metabolites and Their Effect on Complement, RAW 264.7 Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017;18(3):E584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030584
- Viapiana A, Wesolowski M. The Phenolic Contents and Antioxidant Activities of Infusions of Sambucus nigra L. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition. 2017;72(1):82-87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-016-0594-x
- Ho GTT, Zou YF, Aslaksen TH, Wangensteen H, Barsett H. Structural characterization of bioactive pectic polysaccharides from elderflowers ( Sambuci flos ). Carbohydrate Polymers. 2016;135:128-137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.08.056
- Merecz-Sadowska A, Sitarek P, Zajdel K, Sztandera W, Zajdel R. Genus Sambucus: Exploring Its Potential as a Functional Food Ingredient with Neuroprotective Properties Mediated by Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024;25(14):7843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147843
- de Rus Jacquet A, Timmers M, Ma SY, et al. Lumbee traditional medicine: Neuroprotective activities of medicinal plants used to treat Parkinson’s disease-related symptoms. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2017;206:408-425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.02.021
- Harokopakis E, Albzreh MH, Haase EM, Scannapieco FA, Hajishengallis G. Inhibition of Proinflammatory Activities of Major Periodontal Pathogens by Aqueous Extracts From Elder Flower (Sambucus nigra). Journal of Periodontology. 2006;77(2):271-279. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2006.050232
- American Botanical Council (ABC). Elderflower – Herbal Medicine Expanded German E Commission Monographs. Herbalgram.org. Published 2024. Accessed October 18, 2024. http://cms.herbalgram.org/expandedE/Elderflower.html?ts=1593010419&signature=6eabcd8b54284fd612f3f9fa8f0b116f
- Stapley C. The Tree Dispensary. Aeon Books; 2021.
- Natural Medicines. Elderflower. naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com. Published 2024. https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com/databases/food
- Trust W. How to Identify and Use Elderflower. Woodland Trust. https://www.woodlandtrust.org.uk/blog/2021/06/how-to-identify-elder/
- Royal Botanical Gardens Kew. Sambucus nigra L. | Plants of the World Online | Kew Science. Plants of the World Online. Published 2024. https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:30122169-2
- Nature Serve Explorer. Sambucus nigra. Natureserve.org. Published 2024. Accessed October 18, 2024. https://explorer.natureserve.org/Taxon/ELEMENT_GLOBAL.2.638798/Sambucus_nigra
- Bilz M. Sambucus nigra: Bilz, M. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Published online October 7, 2019. https://doi.org/10.2305/iucn.uk.2020-1.rlts.t61684a88328586.en
- Heinrich M, Barnes J, José M Prieto Garcia, et al. Fundamentals of Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy. Elsevier; 2018.
- Evans WC, Trease GE, Evans D. Trease and Evans’ Pharmacognosy. 16th ed. Saunders/Elsevier; 2009.
- British Pharmacopoeia Commission. British Pharmacopoeia 2025. London TSO; 2025.
- Nawirska-Olszańska A, Kolniak-Ostek J, Zubaidi MA, Maksimowski D, Pavla Brandova, Maciej Oziembłowski. Elderflowers (Sambuci flos L.): A Potential Source of Health-Promoting Components. Foods. 2024;13(16):2560-2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162560
- BBC Gardener’s World. How to grow elder. BBC Gardeners World Magazine. Published 2021. https://www.gardenersworld.com/how-to/grow-plants/how-to-grow-elder/
































 Not only can Elderflower be used in acute and first aid situations as discussed above, but elderflower also has a gently relaxant effect which may be applied for those experiencing nightmares and disturbed sleep, useful for both adults and children.
Not only can Elderflower be used in acute and first aid situations as discussed above, but elderflower also has a gently relaxant effect which may be applied for those experiencing nightmares and disturbed sleep, useful for both adults and children. Much of the research available into the immunological effects of Elder, focuses on the elderberry. However an in vitro study on both extracts of Elderberry and Elderflower constituents exhibited promising inflammatory modulating activity. It must be noted though that unfortunately clinical trials are lacking for elderflower.
Much of the research available into the immunological effects of Elder, focuses on the elderberry. However an in vitro study on both extracts of Elderberry and Elderflower constituents exhibited promising inflammatory modulating activity. It must be noted though that unfortunately clinical trials are lacking for elderflower.







